Unlocking the Mystery: How Do We Take Blood Pressure?
Have you ever wondered about the process behind measuring blood pressure? Understanding how this vital sign is taken is crucial for monitoring health. Whether you’ve encountered the procedure at the doctor’s office or are simply curious, delve into this comprehensive guide to demystify the steps involved in taking blood pressure.

Understanding the Importance of Blood Pressure Measurements
Measuring blood pressure is crucial in monitoring cardiovascular health. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to serious health issues like heart disease and stroke. On the other hand, low blood pressure can cause dizziness and fainting. Regular blood pressure measurements help identify any potential problems early, allowing for timely intervention and management.
When understanding blood pressure readings, it’s essential to know the two numbers involved: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). Systolic pressure measures the force on the arteries when the heart beats, while diastolic pressure measures the force when the heart is at rest between beats. The American Heart Association recommends maintaining a blood pressure below 120/80 mm Hg.
To accurately measure blood pressure, it’s advisable to use a reliable blood pressure monitor. Automatic digital monitors are commonly used for home monitoring, providing convenience and accuracy. These monitors typically inflate a cuff on your arm and then gradually release the pressure while detecting your blood pressure levels.
Understanding your blood pressure measurements empowers you to take control of your health. By regularly monitoring your blood pressure levels and making lifestyle adjustments as needed, such as diet changes, exercise, and stress management, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular conditions.
Consulting with healthcare professionals for interpreting blood pressure readings and creating a personalized management plan is crucial for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. Awareness, monitoring, and proactive measures can play a significant role in preventing potential health complications associated with high or low blood pressure.
Exploring the Tools Used to Measure Blood Pressure
Various tools are available for measuring blood pressure accurately. The traditional tool used by healthcare providers is the sphygmomanometer, which consists of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope. This manual device requires proper training to use effectively but is highly accurate when utilized correctly.
On the other hand, automatic digital blood pressure monitors are user-friendly devices commonly utilized at home. These devices are easy to operate, provide digital readings, and store data for tracking purposes. They come in wrist or arm cuff forms and offer convenience and precision for routine monitoring.
When exploring blood pressure measurement tools, it’s essential to consider factors like cuff size, accuracy, ease of use, and memory capability. Choosing a device that fits your arm size correctly and provides accurate readings consistently is vital for monitoring blood pressure effectively.
Additionally, some advanced blood pressure monitors offer features like irregular heartbeat detection, multiple user profiles, and connectivity to smartphone apps for data management. Exploring these advanced tools can enhance your monitoring experience and provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular health status.
By understanding the tools available for measuring blood pressure and selecting one that suits your needs, you can establish a regular monitoring routine at home, promoting proactive health management and empowering you to make informed decisions regarding your cardiovascular well-being.
Step-by-Step Guide to Taking Accurate Blood Pressure Readings
Step 1: Prepare the Environment
Choose a quiet room and sit comfortably in a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Rest for 5 minutes before taking the measurement to ensure accuracy.
Step 2: Proper Placement of the Cuff
Place the cuff on your bare arm with the bottom edge about an inch above your elbow. Ensure the cuff fits snugly but not too tight, and the monitor is at heart level.
Step 3: Taking the Reading
Press the start button on the blood pressure monitor, and remain still while it inflates and deflates. Note the systolic and diastolic numbers displayed on the screen.
Step 4: Record and Interpret the Results
Write down your blood pressure readings along with the date and time. Compare the values to the recommended ranges and consult a healthcare provider if needed for further guidance.
Step 5: Maintain a Monitoring Schedule
Establish a routine for monitoring your blood pressure regularly, whether daily or weekly, to track trends and changes over time. Use the recorded data to assess the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications and treatments.
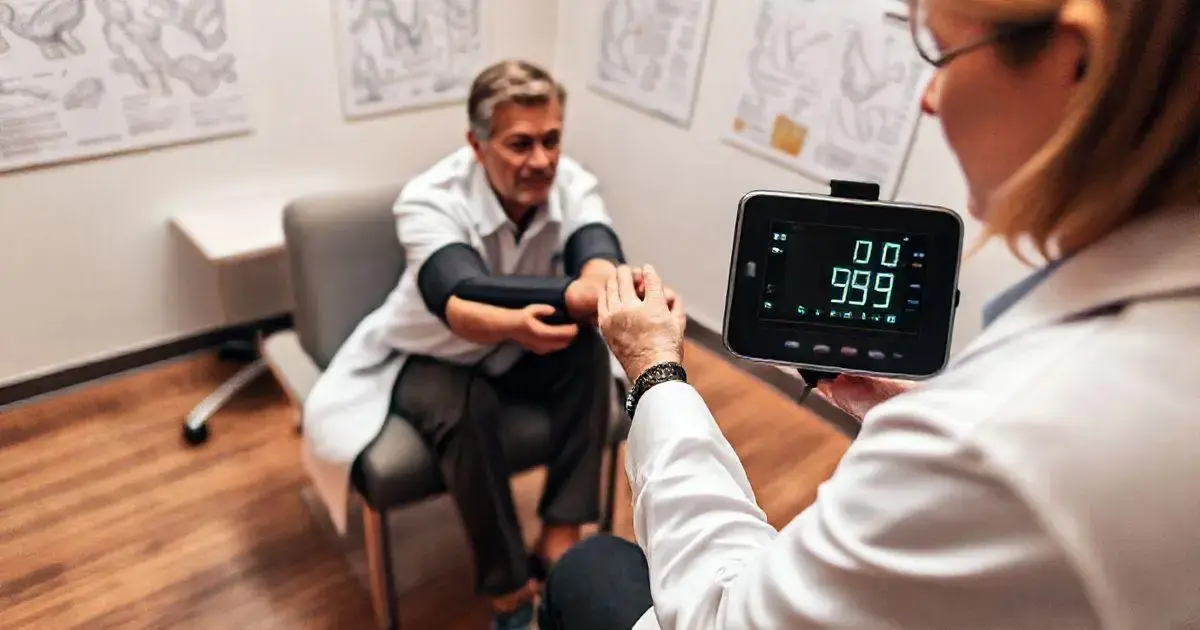
Techniques for Proper Blood Pressure Measurement
Proper blood pressure measurement is crucial for accurate health assessments. Here are the steps on how to take blood pressure correctly:
Selecting the Right Equipment
Start by choosing a high-quality blood pressure monitor. Ensure it is calibrated and validated for accurate readings. The cuff size should fit the individual’s arm properly.
Preparing for Measurement
Before taking blood pressure, ensure the individual is relaxed and has not consumed caffeine or tobacco in the last 30 minutes. They should sit in a comfortable position with their back supported.
Positioning the Individual
The individual’s arm should be supported at heart level on a flat surface. Make sure their feet are flat on the ground, legs uncrossed, and back straight.
Taking the Measurements
Wrap the blood pressure cuff snugly around the individual’s upper arm. Place the stethoscope below the cuff’s edge over the brachial artery. Inflate the cuff and slowly deflate while listening for the heartbeat.
Recording the Results
Record the systolic and diastolic readings accurately. Repeat the process for consistency or if the initial reading seems off. Document the time and date of the measurement.
Common Mistakes When Taking Blood Pressure
Several errors can lead to inaccurate blood pressure readings. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when measuring blood pressure:
Incorrect Cuff Placement
Placing the cuff in the wrong position can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure the cuff is positioned on the upper arm at heart level for precise measurements.
Talking During Measurement
Engaging in conversation during the blood pressure reading can elevate readings. Advise the individual to remain quiet and relaxed until the measurement is complete.
Inadequate Rest Period
Not allowing the individual to rest before measurement can result in higher readings. Ensure they sit quietly for at least 5 minutes before taking blood pressure.
Improper Cuff Size
Using the wrong cuff size can lead to erroneous readings. Verify the correct cuff size based on the individual’s arm circumference to ensure accuracy.
Relying on Single Reading
Depending on a single reading may not provide an accurate representation of the individual’s blood pressure. Take multiple readings and calculate the average for a more reliable measurement.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure Accuracy
Several elements can influence the accuracy of blood pressure measurements. Understanding these factors is essential for precise readings:
Physical Activity
Engaging in physical activities such as exercise right before measuring blood pressure can temporarily elevate readings. Advise individuals to refrain from vigorous activities before measurements.
Mental Stress
Stress and anxiety can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure. Encourage individuals to relax and remain calm before and during the measurement to prevent inaccuracies.
Cuff Positioning
Incorrect cuff positioning can affect the accuracy of measurements. Ensure the cuff is placed correctly on the upper arm at heart level to obtain reliable readings.
Caffeine and Tobacco
Consuming caffeine or tobacco products can lead to temporary increases in blood pressure. Advise individuals to avoid these substances before measuring blood pressure.
White-Coat Hypertension
Some individuals may experience elevated blood pressure in a clinical setting due to anxiety. Consider using ambulatory monitoring to eliminate white-coat hypertension effects for accurate readings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the importance of blood pressure measurements is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health. By recognizing the significance of both systolic and diastolic readings, individuals can better manage their health and mitigate risks associated with hypertension and hypotension. Regular monitoring not only facilitates early detection of potential health issues but also empowers individuals to take proactive measures in their daily routines.
Choosing the right blood pressure monitoring device and employing proper techniques is essential for obtaining accurate readings. From familiarizing oneself with equipment to maintaining a calm environment during measurements, these practices contribute significantly to the validity of the results. Awareness of common errors and factors that may affect blood pressure accuracy further enhances the reliability of health assessments.
Ultimately, consulting healthcare professionals is crucial for interpreting blood pressure readings and formulating personalized management plans. By committing to consistent monitoring and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can take control of their cardiovascular wellbeing. Staying informed and proactive lays the foundation for a healthier future and reduces the likelihood of serious health complications.
