Are you concerned about your oral health and wondering “How to Determine If You Have Gum Disease”? Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding your teeth. It is essential to be able to recognize the signs and symptoms early to prevent further complications.
One way to determine if you have gum disease is by checking for symptoms such as red, swollen, or tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, and receding gums. If you notice any of these signs, it is important to consult with your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and intervention are key to managing gum disease effectively and maintaining good oral hygiene.
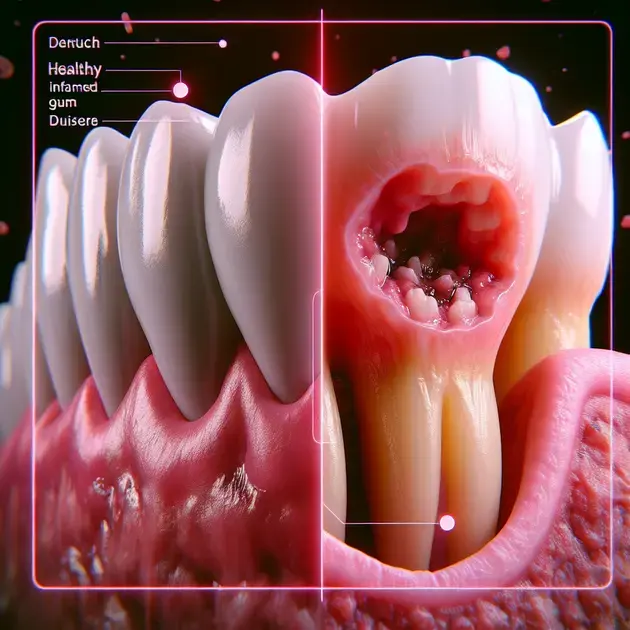
Signs of Gum Disease to Watch For
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that can lead to serious complications if left untreated. It is important to be aware of the signs of gum disease so that you can seek treatment as early as possible. Some common signs of gum disease to watch for include:
- Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
- Swollen or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Persistent bad taste in the mouth
Steps to Check for Gum Disease:
To check for signs of gum disease, you can use a mirror to examine your gums for any of the above symptoms. You can also use a dental probing tool to measure the depth of the pockets between your teeth and gums, which can indicate the presence of gum disease. If you notice any of these signs, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist for a proper diagnosis.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of gum disease is crucial for preventing further damage to your gums and teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can progress and lead to more serious oral health issues, such as tooth loss and bone damage. By being proactive and seeking treatment early, you can prevent the progression of gum disease and maintain good oral health.
How to Detect Gum Disease Early:
One way to detect gum disease early is to visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist will be able to spot the signs of gum disease before it becomes a more serious problem. Additionally, practicing good oral hygiene at home, including brushing and flossing regularly, can help prevent gum disease and catch it early.
Consulting a Dentist for Diagnosis
If you suspect that you may have gum disease, it is important to consult a dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. A dentist will be able to assess the severity of your gum disease and recommend the appropriate course of action to address it. This may include deep cleaning, medication, or in more severe cases, surgery.
Where to Find a Dentist:
To find a dentist for diagnosis and treatment of gum disease, you can use online platforms such as Zocdoc or Healthgrades to search for dentists in your area. Simply enter your location and search for dentists specializing in periodontics or gum disease treatment. Make sure to read reviews and ratings to choose a dentist who is experienced and trustworthy.

Common Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. It is important to be aware of the common symptoms of gum disease so that you can seek treatment as soon as possible. One of the most common symptoms of gum disease is bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing. This is often a sign of inflammation and infection in the gums.
Another symptom of gum disease is bad breath that doesn’t go away even with regular brushing and mouthwash. This is caused by the bacteria in the mouth that are associated with gum disease. Additionally, gum disease can cause gums to become red, swollen, and tender to the touch. If you notice these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist promptly for an evaluation.
As gum disease progresses, it can lead to receding gums and even tooth mobility. You may also experience pain when chewing or sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. In advanced stages, gum disease can cause pus between the teeth and gums and eventually result in tooth loss.
To prevent gum disease, it is essential to practice good oral hygiene, including brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, do not hesitate to seek professional help to prevent further complications.
Preventive Measures for Gum Health
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health, and there are several preventive measures you can take to ensure gum health. One of the most important preventive measures is to practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth.
In addition to regular oral hygiene practices, it is essential to eat a balanced diet low in sugary foods and drinks. Sugary substances can contribute to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding tobacco products are also beneficial for gum health.
Another preventive measure for gum health is to schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide appropriate treatment to prevent it from progressing. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria in the mouth and promote gum health.
If you are at a higher risk of developing gum disease due to factors such as smoking, diabetes, or a family history of gum problems, it is crucial to be extra vigilant about preventive measures. By taking proactive steps to care for your gums, you can reduce the risk of gum disease and maintain a healthy smile for years to come.
Understanding the Treatment Options
When it comes to treating gum disease, there are several options available depending on the severity of the condition. In the early stages of gum disease, known as gingivitis, treatment typically involves professional dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Your dentist may also recommend improved oral hygiene practices at home.
If gum disease has progressed to a more advanced stage, such as periodontitis, more intensive treatments may be necessary. This can include scaling and root planing to clean the roots of the teeth and promote gum reattachment. In some cases, surgical interventions may be required to address deep pockets or bone loss.
Antibiotics or antimicrobial mouth rinses may be prescribed to help control infection and inflammation associated with gum disease. Your dentist may also recommend lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or managing conditions like diabetes, to improve gum health. In severe cases, tooth extraction may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
It is essential to consult with your dentist to understand the best treatment options for your specific case of gum disease. By addressing the condition promptly and following the recommended treatment plan, you can prevent further damage to your gums and maintain good oral health in the long run.
Conclusion
Understanding the common symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment to prevent serious consequences like tooth loss. Bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, gum inflammation, and tooth sensitivity are key indicators that should not be ignored. It is imperative to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, to minimize the risk of developing gum disease.
Preventive measures play a vital role in promoting gum health and overall oral well-being. Practicing proper oral hygiene, following a balanced diet low in sugary foods, staying hydrated, and avoiding tobacco products are essential steps to prevent gum disease. Scheduling regular dental visits for cleanings and check-ups, along with using antimicrobial mouthwash, can further aid in reducing the risk of gum problems.
When it comes to treating gum disease, the options vary based on the disease’s severity. From professional cleanings and improved home care for gingivitis to more advanced treatments like scaling, root planing, and surgical interventions for periodontitis, seeking professional guidance is crucial. Following prescribed treatments, making necessary lifestyle changes, and collaborating closely with your dentist can lead to effective management of gum disease and the preservation of long-term oral health.
